Radiant Energy Definition - What Exactly Is Radiant Energy?
The term "radiant energy" is most commonly used in the fields of radiometry, solar energy, heating and lighting, but is also sometimes used in other fields (such as telecommunications). In modern applications involving transmission of power from one location to another, "radiant energy" is sometimes used to refer to the electromagnetic waves themselves, rather than their energy (a property of the waves). In the past, the term "electro-radiant energy" has also been used.
The term "radiant energy" also applies to gravitational radiation. For example, the first gravitational waves ever observed were produced by a black hole collision that emitted about 5.3×1047 joules of gravitational-wave energy.
Learn more: Self-powered electrical generator: The nature of electrical impulses to generate radiant energy
See more details here: Unraveling Nikola Tesla's Greatest Secret: Radiant Energy
On a small scale, the exploitation of radiant energy in the form of cold electricity - Tesla was successful.
This is a video about the construction of a generator - radiant energy - cold electricity
Build a Free Energy Generator based on the Diagram - Radiant Energy
The term "radiant energy" also applies to gravitational radiation. For example, the first gravitational waves ever observed were produced by a black hole collision that emitted about 5.3×1047 joules of gravitational-wave energy.
What Exactly Is Radiant Energy?
Radiant Energy by mainstream science
Mainstream science:
In physics, and in particular as measured by radiometry, radiant energy is the energy of electromagnetic and gravitational radiation. As energy, its SI unit is the joule (J). The quantity of radiant energy may be calculated by integrating radiant flux (or power) with respect to time. The symbol Qe is often used throughout literature to denote radiant energy ("e" for "energetic", to avoid confusion with photometric quantities). In branches of physics other than radiometry, electromagnetic energy is referred to using E or W. The term is used particularly when electromagnetic radiation is emitted by a source into the surrounding environment. This radiation may be visible or invisible to the human eye.
Analysis:
Because electromagnetic (EM) radiation can be conceptualized as a stream of photons, radiant energy can be viewed as photon energy – the energy carried by these photons. Alternatively, EM radiation can be viewed as an electromagnetic wave, which carries energy in its oscillating electric and magnetic fields. These two views are completely equivalent and are reconciled to one another in quantum field theory - see wave-particle duality.
EM radiation can have various frequencies. The bands of frequency present in a given EM signal may be sharply defined, as is seen in atomic spectra, or may be broad, as in blackbody radiation. In the photon picture, the energy carried by each photon is proportional to its frequency. In the wave picture, the energy of a monochromatic wave is proportional to its intensity. This implies that if two EM waves have the same intensity, but different frequencies, the one with the higher frequency "contains" fewer photons, since each photon is more energetic.
When EM waves are absorbed by an object, the energy of the waves is converted to heat (or converted to electricity in case of a photoelectric material). This is a very familiar effect, since sunlight warms surfaces that it irradiates. Often this phenomenon is associated particularly with infrared radiation, but any kind of electromagnetic radiation will warm an object that absorbs it. EM waves can also be reflected or scattered, in which case their energy is redirected or redistributed as well.
Open systems:
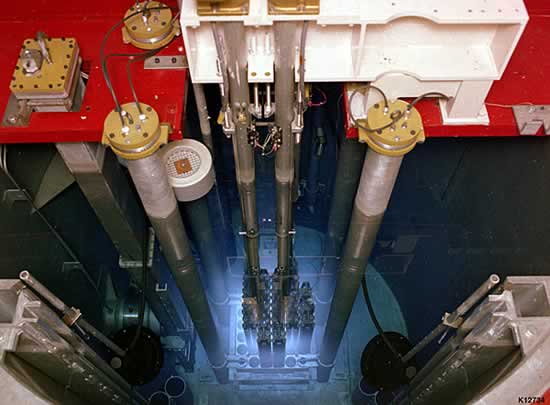
Radiant energy is one of the mechanisms by which energy can enter or leave an open system. Such a system can be man-made, such as a solar energy collector, or natural, such as the Earth's atmosphere. In geophysics, most atmospheric gases, including the greenhouse gases, allow the Sun's short-wavelength radiant energy to pass through to the Earth's surface, heating the ground and oceans. The absorbed solar energy is partly re-emitted as longer wavelength radiation (chiefly infrared radiation), some of which is absorbed by the atmospheric greenhouse gases. Radiant energy is produced in the sun as a result of nuclear fusion.
Radiant Energy by People outside of mainstream science
In 1875, Sir William Crookes discovered the properties of Radiant Matter. His invention of the Radiometer was proof that Radiant Matter was a constituent of sunlight. Nikola Tesla, following up on these discoveries, found that electrostatic charges could also be conveyed by Radiant Matter. He called it Radiant Energy. When Radiant Energy was transmitted from place to place, it behaved like “sound waves of electrified air.” By 1900, Tesla had developed lighting systems and electric motors that ran on Radiant Energy. By 1934, Thomas Henry Moray had demonstrated a small box that produced 50,000 watts, running on Radiant Energy. In 1973, Edwin V. Gray started demonstrating his EMA motor, an 80hp electric motor capable of keeping its own batteries charged while delivering surplus mechanical energy. And Paul Baumann built numerous models of an astonishing self-running machine called “Testatika” in Switzerland in the 1980’s. Much of John Bedini‘s work also falls into the field of Radiant Energy. These developments are only the tip of the iceberg in our knowledge of what is mistakenly referred to as “static electricity” but is really something much more astonishing.
Abnormal DC phenomena are clues to harness Radiant Energy:
Before Tesla's invention of the Polyphase AC generator became the industry standard and overtook Thomas Edison's use of DC generators, the DC electrical system was the only system available to deliver electricity to America's homes and factories.
Due to the resistance offered by long transmission lines, Edison had to produce very high DC voltages from his generators in order to deliver enough voltage and current to its final destination. He also had to provide additional 'pumping' stations along the way to boost the sagging voltage which dwindled from line losses.
A curious anomaly occurred in the very first instant of throwing the power switch at the generating station: Purple/blue colored spikes radiated in all directions along the axis of the power lines for just a moment. In addition, a stinging, ray-like shocking sensation was felt by those who stood near the transmission lines.
In some cases, when very large DC voltages surged from the generators, the "stinging" sensation was so great that occasionally a blue spike jumped from the line and grounded itself through a workman, killing him in the process.
Tesla realized almost immediately that electrons were not responsible for such a phenomena because The blue spike phenomena ceased as soon as the current stated flowing in the lines. Something else was happening just before the electrons had a chance to move along the wire.
At the time, no one seemed to be very interested in discovering why these dramatic elevations in static electrical potential were taking place, but rather, engineering design efforts were focused on eliminating and quenching this strange anomaly which was considered by everyone to be a nuisance-except Tesla.
Tesla viewed it as a powerful, yet unknown form of energy which needed to be understood and harnessed if possible. The phenomena only exhibited itself in the first moment of switch closure, before the electrons could begin moving.
There seemed to be a "bunching" or "choking" effect at play, but only briefly. Once the electrons began their movement within the wire, all would return to normal. What was this strange energy that was trying to liberate itself so forcefully at the moment of switch closure?
Learn more: Self-powered electrical generator: The nature of electrical impulses to generate radiant energy
Radiant Energy and Cold Electricity
Later, the abnormal DC phenomenon was developed by Tesla into a spark gap in the Tesla coil. With circuits that have a spark gap (similar to anomalous DC), Tesla has created a technology to transmit electricity wirelessly and harness energy from the sky (from nothingness). The intention to develop Radiant Energy to provide electricity to all mankind cheap (or free) has been suppressed by "energy monopoly".
The smallest scale of Radiant Energy is Cold Electricity. Experiments on refrigeration show that electricity can be transmitted without elets. This is a Radiant Energy.
See the transmission of Radiant Energy (Cold Electricity form):
Up to now, official science has not been funded to study Radiant Energy - Cold Electricity. Here is a comment and explanation in the theory of Electric Universe:
I'm definitely not an expert but I'm at least pretty sure... But not 100% sure... That in order to have a dielectric discharge there must be a insulating dielectric barrier ....which is why high voltage is required to do it....and dielectric discharge produces ozone....and since the earth has a ozone layer... You must conclude that the universe is electrical and not gravitational which is quite obvious to people outside of mainstream science... They will never admit that the universe and sun are in fact electric... And they will never get rid of Einsteins obviously incorrect theory because of 1 reason...if they do admit it then they will be admitting that they have been fear mongering citizens of the World with nuclear weapons and that nuclear weapons are fake....because they are based on Einsteins incorrect gravitational sun model were explosives are placed around a core and detonated squeezing the core... Just like how they claimed the sun worked... The electric universe theory explains the universe very easily unlike the standard model...its no comparison... The electric universe theory blows the standard model away in terms of simplicity and explanation of the universe... (Source)
What are the Applications of radiant energy?
Applications of radiant energy by mainstream science
Radiant energy is used for radiant heating. It can be generated electrically by infrared lamps, or can be absorbed from sunlight and used to heat water. The heat energy is emitted from a warm element (floor, wall, overhead panel) and warms people and other objects in rooms rather than directly heating the air. Because of this, the air temperature may be lower than in a conventionally heated building, even though the room appears just as comfortable.
Various other applications of radiant energy have been devised. These include treatment and inspection, separating and sorting, medium of control, and medium of communication. Many of these applications involve a source of radiant energy and a detector that responds to that radiation and provides a signal representing some characteristic of the radiation. Radiant energy detectors produce responses to incident radiant energy either as an increase or decrease in electric potential or current flow or some other perceivable change, such as exposure of photographic film
Applications of Radiant energy by People outside of mainstream science
Application in Medicine
The Tesla coil produces Radiant Energy, and it has been used in physiotherapy. Electric current can be transmitted through the human body, but the patient does not feel the electric shock.
Application in exploiting electricity
Tesla's intention is to develop Radiant Energy to provide cheap electricity to mankind on a large scale. However, the work was suppressed.See more details here: Unraveling Nikola Tesla's Greatest Secret: Radiant Energy
On a small scale, the exploitation of radiant energy in the form of cold electricity - Tesla was successful.
This is a video about the construction of a generator - radiant energy - cold electricity
Build a Free Energy Generator based on the Diagram - Radiant Energy
Maybe you like: Zero Point Energy Of The Permanent Magnet
Practical guide
✰* Revealed At Last: Ancient Invention Generates Energy-On-Demand
✔ Nikola Tesla’s method of magnifying electric power by neutralizing the magnetic counter-forces in an electric generator
✔ Currents are 180 out of phase with each other, Lenz's law naturally is broken
✔ Principle of Resonance to achieve Overunity
Practical guide
✰* Revealed At Last: Ancient Invention Generates Energy-On-Demand
✔ Nikola Tesla’s method of magnifying electric power by neutralizing the magnetic counter-forces in an electric generator
Generates Energy-On-Demand: Easy Power Plan Will Change Our World Forever
✔ Currents are 180 out of phase with each other, Lenz's law naturally is broken
✔ Principle of Resonance to achieve Overunity
Radiant Energy Definition - What Exactly Is Radiant Energy?
 Reviewed by Re-programming Life
on
4:49 AM
Rating:
Reviewed by Re-programming Life
on
4:49 AM
Rating:
 Reviewed by Re-programming Life
on
4:49 AM
Rating:
Reviewed by Re-programming Life
on
4:49 AM
Rating:




















Ak by mala byť pravda, čo sa píše v článku, neviem, prečo sa používa ešte palivo, ako je uhlie, drevo, alebo plyn.
ReplyDelete